What Is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
Fetal alcohol syndrome is a disorder that develops in a child as a result of the mother’s alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
Alcohol consumption during pregnancy can result in the birth of kids with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders, or FASDs. FASD is a cover name for a variety of conditions. These disorders can range in severity from mild to severe, and they can result in physical and mental birth problems. FASDs come in a variety of forms, including:
- Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS): the alcohol is transmitted via your circulation to the fetal via the umbilical cord is one of the reasons why it is hazardous during pregnancy
- Partial fetal alcohol syndrome (pFAS): People with pFAS have some of the features of FAS (for example, alterations in facial features), but not all of the symptoms.
- Alcohol-related birth defects (ARBD): Physical birth defects (abnormal changes to components of the body) that can damage the heart, eyes, skeletal system, hearing, and kidneys are known as (ARBD).
- Alcohol-related neurodevelopment disorder (ARND): People with this illness have impulsivity, inattentiveness, and problems with judgment and school performance, to name a few symptoms.
- A neurobehavioral disorder associated with prenatal alcohol exposure (ND-PAE): As a fetus, someone with this syndrome was exposed to a significant amount of alcohol. Because of serious behavior concerns such as severe tantrums, they have difficulty with basic tasks such as bathing and may struggle in social situations. They also have difficulty thinking and remembering things.
FAS is an extremely severe type of disease. FAS patients may experience difficulties with their vision, hearing, memory, mental concentration, and learning and communication abilities. While the defects differ from person to person, the damage is frequently permanent. FAS and other spectrum illnesses have varied effects on children. The signs and symptoms might be modest to severe. They may include the following:
- Heart, renal, and bone problems are all common.
- Low IQ and learning disabilities
- Memory, coordination, and concentration issues
- Hyperactivity
- As an infant, I had sleep and suckling issues
- As a person grows older, the symptoms of fetal alcohol syndrome tend to worsen.
What causes Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)?
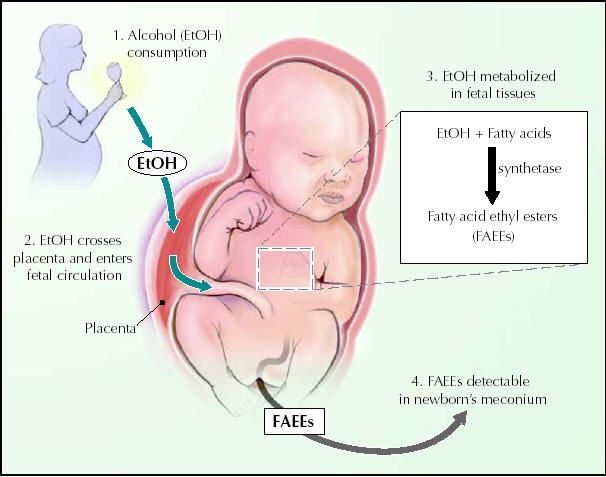
In the United States, alcohol is the greatest main risk factor for birth defects, including wine, beer, and liquor. Because a baby’s liver isn’t fully matured in the womb to process or break down alcohol, it can readily reach and harm the baby’s organs. This can lead to:
- Miscarriage– During the first few months of pregnancy, you may misplace your baby.
- Abortion- During the second half of your pregnancy, you may lose your baby in the womb.
- Prematurely born– Drinking alcohol can cause your baby to arrive prematurely. Premature babies are prone to a variety of health issues. Breathing problems and other complications associated with undeveloped lungs are common.
- Defects in the womb– Some babies are born with issues with their hearts or kidneys. Others may be unable to see or hear.
When a pregnant woman drinks during the first pregnancy, when the baby’s brain is still developing, some of the most serious complications occur. However, the second and third trimesters are not without risk. The brain is still developing at that time, and even moderate doses of alcohol can cause this process to be interrupted.
There is no such thing as a “safe” amount of alcohol for pregnant women to drink. There is also no time when it is observed safe to consume alcohol while pregnant.
What are the Symptoms of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
Because fetal alcohol syndrome covers such a broad range of issues, there are numerous possible symptoms. These symptoms can range in severity from moderate to severe, and they can include:
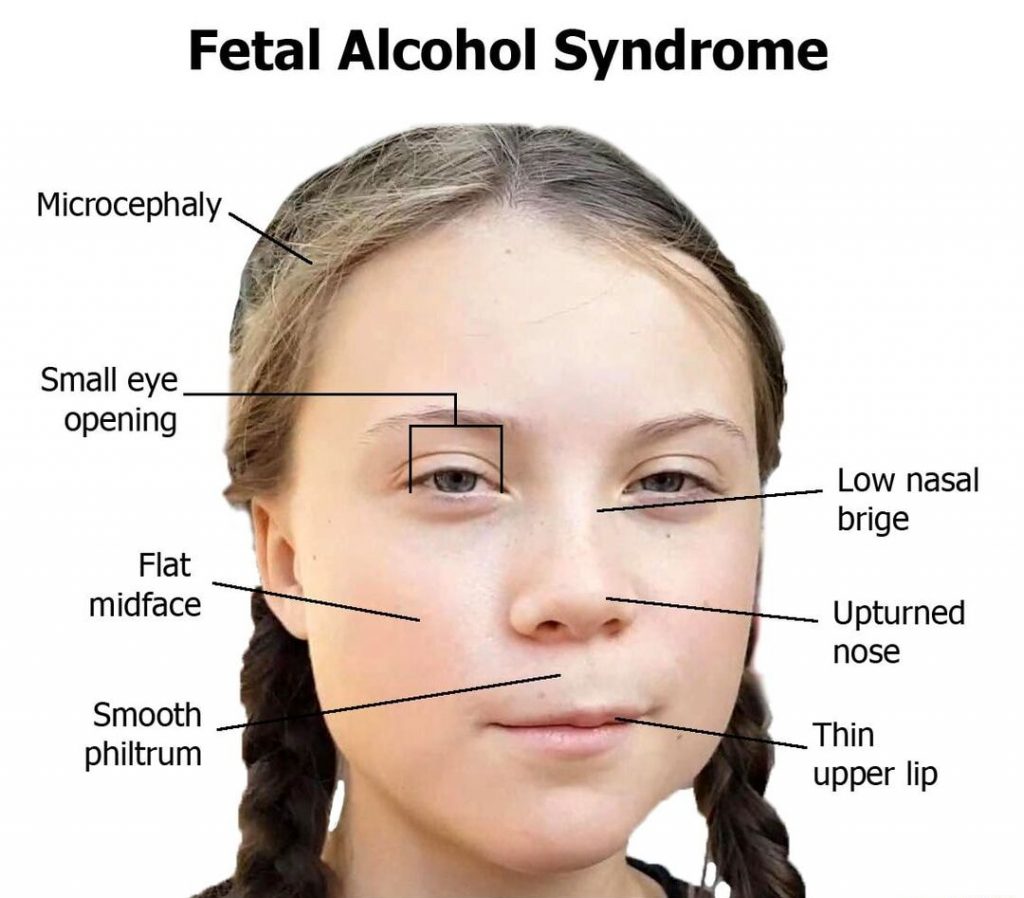
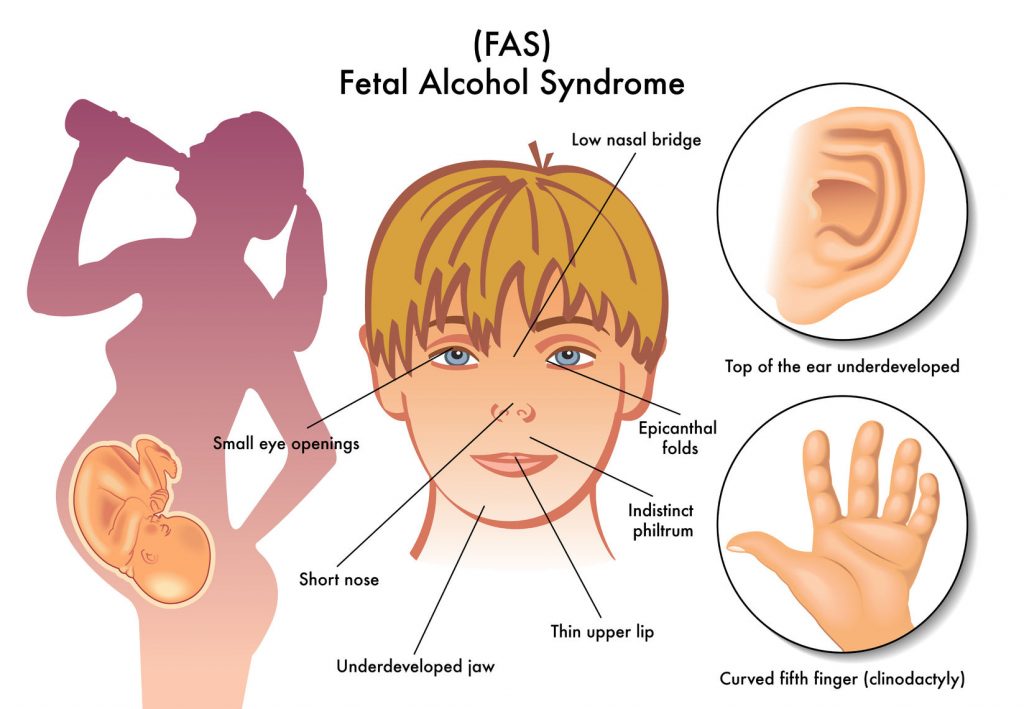
- A small head, a ridge between the upper lip and the nose, small and wide-set eyes, a very thin upper lip, or other atypical facial features
- Below average height and weight
- Hyperactivity
- Inability to concentrate
- A lack of coordination
- Problems with thinking, speech, mobility and social abilities are all symptoms of delayed development.
- Issues with poor judgment learning problems due to sight or hearing
- Intellectual disability
- Issues with the heart
- Abnormalities and defects in the kidneys
- Limbs or fingers that have been distorted
- Swings in mood
How is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome diagnosed?
There is no way of telling if a child has fetal alcohol syndrome without a lab test. Many of its symptoms are comparable to those of ADHD. If you suspect your child has FAS, consult your doctor. If you drank while you were pregnant, tell your doctor.
A physical examination of the infant may reveal a cardiac murmur or other issues with the heart. Other indicators that help confirm the diagnosis may emerge as the infant grows older. These are some of them:
- Growing at a slow speed
- Aberrant bone development or facial features
- Issues with hearing and vision
- Tiny head size and slow language acquisition
- A lack of cooperation
To diagnose FAS, a doctor must find that the patient has atypical facial traits, delayed growth, and abnormalities in the central nervous system. Physical and behavioral issues with the neurological system are possible. They may manifest as agitation or a lack of coordination.
Although fetal alcohol syndrome symptoms cannot be cured, early detection and treatment can help a child’s growth and outlook. According to a study, kids do better when they:
- Are diagnosed before the age of 6
- During their school years, they live in a loving, developing, and constant environment
- Aren’t subjected to abuse
- Receive special education as well as social services.
What are the Treatments for Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
Although FAS is a lifelong condition, some symptoms can be controlled. The sooner you get a diagnosis, the more time you have to make progress. Depending on their symptoms, a child with FAS may require multiple doctors or specialist visits. Special education and social assistance can be beneficial to very young children. Speech therapists, for example, can assist toddlers in learning to communicate.
1. Medications
There are no drugs available to treat FAS. Numerous drugs, on the other hand, may help to lighten symptoms. The following drugs are among them:
- Stimulants are used to treat inattention, hyperactivity, and other behavioral disorders. Antidepressants are used to treat sadness and negativity.
- Anxiety and violence are cured with neuroleptics.
- Nervousness is treated with anti-anxiety medicines
2. Counseling
Behavioral training could also be beneficial. Friendship training like the teacher teaches children social skills for connecting with their classmates. Self-control, judgment, and identifying cause and importance may all benefit from executive function training. FAS children may also need academic help.
Parents and siblings may also require help in dealing with the problems that this disease might bring. Talk treatment or support groups can provide this support. Parents can also get parental training that is exactly customized to their children’s desires. Parental training teaches you how to connect with and care for your child in the most effective way possible.
3. Alternative treatments
Alternative remedies are sought by some parents and their children outside of the medical system. Massage and acupuncture are examples of healing treatments (the placement of thin needles into key body areas). Movement techniques, such as exercise or yoga, are also used as alternative treatments.
Treatment for a mother who is addicted to alcohol is also advised. Not only will this help to prevent future fetal alcohol syndrome difficulties in children, but it will also teach the mother how to help their child with fetal alcohol syndrome.
Complications of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Later in life, fetal alcohol syndrome can lead to behavioral issues. These are some of them:
- Depression, anxiety, eating disorders, and other mental health problems are among the most common.
- Abuse of alcohol or other drugs
- Sexually inappropriate behavior
- Inability to complete or stay in school
- Problems with living independently or finding work
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a disorder
- Aggression, rule or law violation and inappropriate social behavior are examples of behavioral issues.
- Suicide, accident, or homicide is all examples of untimely death.
What steps can you take to avoid Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
If you don’t drink alcohol while pregnant, you can avoid fetal alcohol syndrome. If you’re a woman who wants to get pregnant but has a drinking problem, contact a doctor. If you’re a social or light drinker, don’t drink if you’re thinking about getting pregnant soon. Keep in mind that the effects of alcohol might be felt in the first few weeks of pregnancy.
What is the amount of alcohol that produces Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
Fetal alcohol syndrome can be caused by any amount of alcohol consumed during pregnancy. There is no such thing as a safe quantity. Damage to your unborn child can occur at any time during pregnancy. Even having a drink at the start isn’t a good idea. FAS can be caused by any type of alcohol, including beer, wine, cider, and hard liquor.
How can you Prevent Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
- If you believe you have an alcohol problem, seek help before becoming pregnant. Professionals who specialize in addiction treatment are available.
- While attempting to conceive, avoid consuming alcoholic beverages. If you’re still drinking when you find out you’re pregnant or suspect you’re pregnant, you should quit right away.
- While you’re pregnant, stay away from alcohol. Fetal alcohol syndrome does not affect children whose moms do not drink alcohol while pregnant.
- Consider giving up alcohol completely if you’re sexually active and having unprotected sex.
FAQs
Is it safe to drink alcohol while breastfeeding?
The amount of alcohol in breast milk is fairly close to the amount of alcohol in the mother’s blood. Reduced breast milk consumption, changes in neonatal sleep and wake cycles, and a probable delay in motor development at one year of age are all possible outcomes.
What if all I drink is beer and wine coolers?
All alcoholic beverages can harm an unborn child. A 12-ounce beer can contains the same amount of alcohol as a 4-ounce glass of wine or a 1-ounce shot of straight liquor. Furthermore, some alcoholic beverages, such as malt beverages and wine coolers, contain significantly more alcohol than standard beer.
Is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Inherited From Parents?
Fetal alcohol syndrome is not Inherited From Parents. Only if a woman drinks alcohol while pregnant can she get fetal alcohol syndrome. It is currently unknown why certain children are more likely than others to acquire fetal alcohol syndrome if their moms drank during pregnancy.
Conclusions
Because there is no cure for FAS, women who are pregnant or may become pregnant should avoid using alcohol. If you drink while pregnant, your unborn child is at risk of developing fetal alcohol syndrome. During this time, no quantity of alcohol is safe to consume.
